Hair loss is a commonly faced problem that affects millions of people, both female and male, across all ages. Initial signs include a thinning crown or increased shedding during the shower, plunging the person into distress, and affecting their confidence, a study affirms.
While hair loss may sometimes appear in a sudden or unpredictable manner, the key to remember is that it seldom happens without a cause; there are specific factors, internal and external, that raise this concern.
In the prevention of hair loss journey, understanding what factors contribute to it helps make informed decisions. Additionally, identification of these triggers equips one with the knowledge to understand one's own condition and take positive steps for the protection or restoration of hair health.
Want to learn about such factors that make you prone to hair loss?
Read the complete article.
1. Digital Professions and Lifestyle Habits
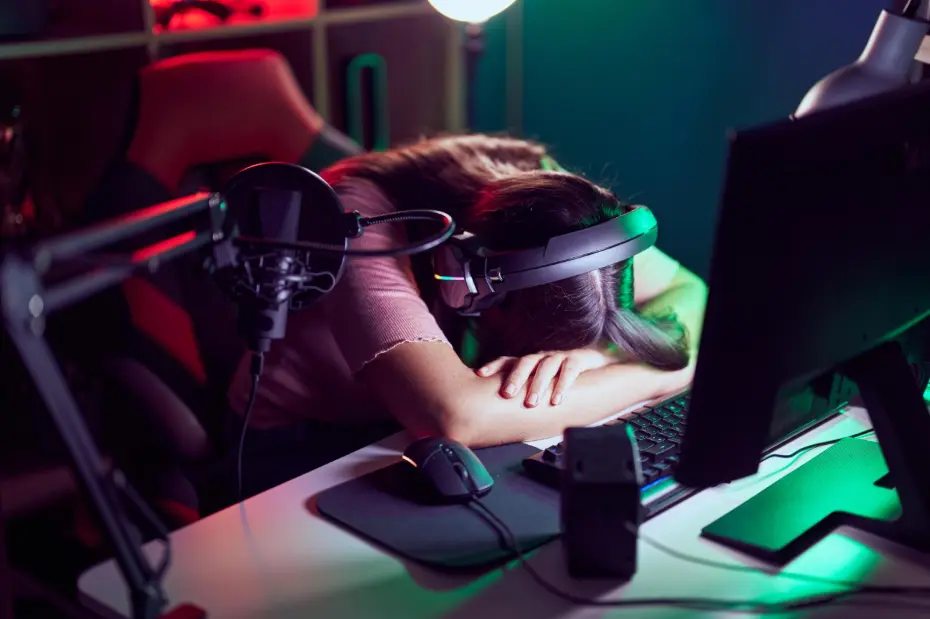

Digital media are hard to resist, often drawing us into long screen hours, impacting our health. Modern digital professions, especially streaming, can make individuals prone to hair loss.
This is because streamers work under pressure, with irregular sleeping patterns, minimal daylight exposure, and extended sitting. All these habits hinder body hormones, weaken your immune system, and eventually cut down the blood supply to your scalp.
Poor diet, a lot of soda and energy drink consumption, coupled with skipped meals, affect your hair health. Additionally, wearing heavy, tight headsets for hours is terrible for the follicles of the temples, ultimately resulting in traction alopecia.
Overall, the aforementioned factors pave the way for hair loss. However, this can be minimized if streamers start incorporating structured routines, good nutrition, regular breaks, and scalp care techniques.
2. Genetic Predisposition
Hair loss is induced due to genetics. There is a certain chance that if hair thinning or baldness runs in your family, you might experience it as well. This condition impacts both males and females and is called androgenetic alopecia.
It is caused by a hormone called DHT, which shortens the life of the hair follicles. Usually, such hair loss begins slowly, causing a receding hairline to appear in men and thinning of the crown in women.
While you can not interfere with your genes, early intervention may help slow down this process. Also, by identifying your family pattern with hair loss, one is better able to watch for changes and consider strategies at an earlier stage to help maintain hair.
3. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones greatly influence the hair growth cycle. Any disruption in hormonal balance causes massive shedding or thinning of hair. Causes can range from age-related conditions, thyroid disorders, PCOS, and menopause that create considerable hair loss to many other conditions.
Moreover, hormonal alterations during pregnancy and postpartum greatly affect hair density in women, whereas hormonal medications (i.e., oral contraceptives) may influence shedding. As a result, in such cases, hair shafts prematurely quit the growth phase and enter the resting phase.
4. Stress and Mental Strain
Emotional stress and psychological strain are a few of the common causes of hair loss but are often neglected by most. As a result, people suffer from conditions like telogen effluvium, which causes hair to enter the resting phase, a common response to stress in the body.
This leads to excessive hair shedding weeks or months after a stressful event. Chronic anxiety, burnout, or trauma can all contribute to it. People may, in extreme cases, develop trichotillomania, a condition where they pull out their hair in frustration or emotional distress.
High-pressure professions or digital careers that do not allow for proper sleep times can exacerbate stress-induced hair problems. Hence, establishing proper sleep hygiene, practicing mindfulness, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can all contribute to maintaining scalp health.
5. Poor Nutrition and Deficiencies
Hair follicles require essential nutrients to function properly. Diets low in vitamins, minerals, and protein can weaken hair structure and slow growth. Common deficiencies linked to hair loss include iron, vitamin D, zinc, and biotin.
A lack of protein can also cause thinning, as hair is primarily made of keratin. People who follow strict diets, eat irregularly, or rely heavily on processed foods may be at higher risk.
Nutritional gaps are prevalent in busy individuals who skip meals or favor convenience overbalance. Incorporating whole foods, lean proteins, and leafy greens can improve scalp nourishment and support healthy hair growth.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle and Circulation Issues
A sedentary lifestyle can negatively affect blood circulation, including to the scalp. Hair follicles rely on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered through the bloodstream.
Sitting for long hours without any physical activity can reduce circulation, potentially weakening follicle function over time. People who work desk jobs or spend extended periods indoors, such as streamers or remote workers, may experience slower hair growth as a result.
Regular movement, stretching, and cardiovascular activity support healthier blood flow. Even simple habits, such as walking during breaks or practicing scalp massage, can enhance circulation.
Improving overall fitness contributes not just to general well-being but also to hair vitality.
7. Styling Damage and Harsh Treatments
Frequent styling, chemical processing, and heat application can contribute to hair damage and loss. Hairstyles that pull tightly, such as ponytails, braids, or buns, can cause traction alopecia, a type of hair loss resulting from constant tension.
Repeated use of flat irons, curling tools, and blow dryers can weaken the hair shaft, causing breakage and thinning. Coloring, bleaching, or perming hair strips it of natural oils and protein, further increasing vulnerability.
In some cases, even wearing tight headphones for extended periods can cause damage to the hair around the temples. Choosing gentler styling techniques and allowing hair to air dry can help prevent unnecessary strain and support regrowth.
8. Medical Conditions and Medications
Several medical conditions can interfere with normal hair growth. Autoimmune disorders, such as alopecia areata, trigger the immune system to attack hair follicles. Scalp infections, chronic illnesses such as lupus or diabetes, and high fevers can also lead to hair shedding.
In addition, specific medications list hair loss as a side effect. These include chemotherapy drugs, antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and hormone therapies.
If you observe hair loss after starting a new medication, consult your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage or recommend alternatives. Addressing the underlying medical issue is key to restoring balance and promoting healthier, more consistent hair growth.
Bottomline
Hair loss can be emotionally tolling, but understanding what makes you more prone to it is the first step toward finding the right solutions.
Whether it’s genetics, stress, poor nutrition, or lifestyle habits, each factor plays a role in how your hair behaves. By recognizing these triggers early, you can take proactive steps to protect your hair and improve overall scalp health.
While not all causes can be reversed, many can be managed with the proper care. However, awareness and action combined can make a significant difference in preserving your hair.